Data Encapsulation, Inheritance, and Polymorphism
Object-oriented programming involves using objects, classes and methods to solve problems. Most object-orientated languages require you to understand the following:
Data Encapsulation: Restricting the manipulation of an object’s state by external users to set of methods calls.
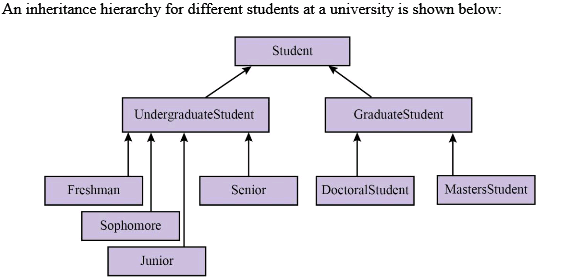
Inheritance: Allows a class to automatically reuse and extend upon the code of similar but more general classes.
The subclass may also extend its parent class by adding data and/or methods or modifying the same methods. Inheritance is a major means of reusing code.
Polymorphism: Allowing several different classes to use the same general method names.
The term ‘polymorphic’ means many bodies, and applies to two methods that have the same header, but have different definitions in different classes.
This reduces the need to learn new names for standard, well understood operations.
All three of the above features of object-oriented programming are essential to simplify programs and make them more maintainable.
